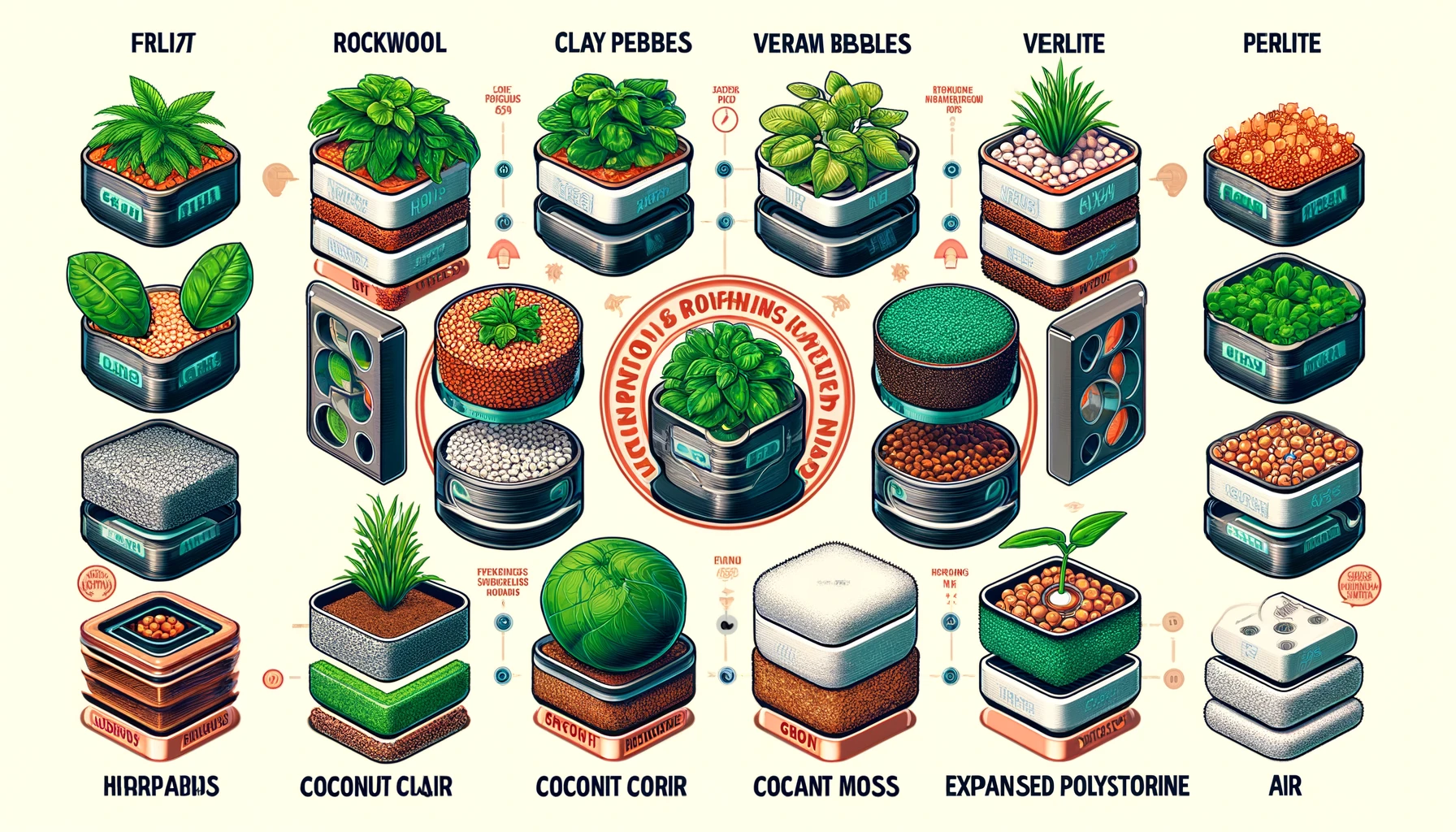
In hydroponics, plants are grown without soil, but they still need a medium to support their roots and facilitate the delivery of nutrients. Here are some common mediums used in hydroponic systems:
- Rockwool: Made from melted rock spun into fiber, Rockwool is widely used for its ability to retain water and air, making it ideal for seed starting and plant growing.
- Clay Pebbles: These are lightweight, porous, and have a neutral pH. They are great for systems where water is recirculated, like in ebb and flow or DWC systems.
- Perlite: A volcanic glass that is expanded and popped through heating, perlite is lightweight and can hold air and water. It’s often mixed with other growing mediums to improve aeration.
- Vermiculite: Similar to perlite, vermiculite has a high water-holding capacity and is often used in seed starting mixes or blended with other mediums.
- Coconut Coir: Made from coconut husk fibers, coconut coir is an excellent medium for retaining moisture and providing a natural, sustainable environment for root development.
- Peat Moss: Known for its ability to retain water, peat moss is often used in hydroponic systems as part of a blended growing medium.
- Expanded Polystyrene: This is a sterile, lightweight material that can be used as floating boards for DWC systems.
- Growstones: Made from recycled glass, Growstones are lightweight and have high porosity, making them suitable for hydroponic systems that require good drainage and air flow.
- Air: In aeroponic systems, roots are suspended in the air and misted with nutrient solution, so technically air serves as the growing medium.
Each of these mediums has unique properties that make them suitable for different types of hydroponic systems and plant needs. The choice of medium depends on factors like water retention, aeration, and the specific requirements of the plants being grown.